Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #455
October 31 - November 6, 2025, by Elm Analytics
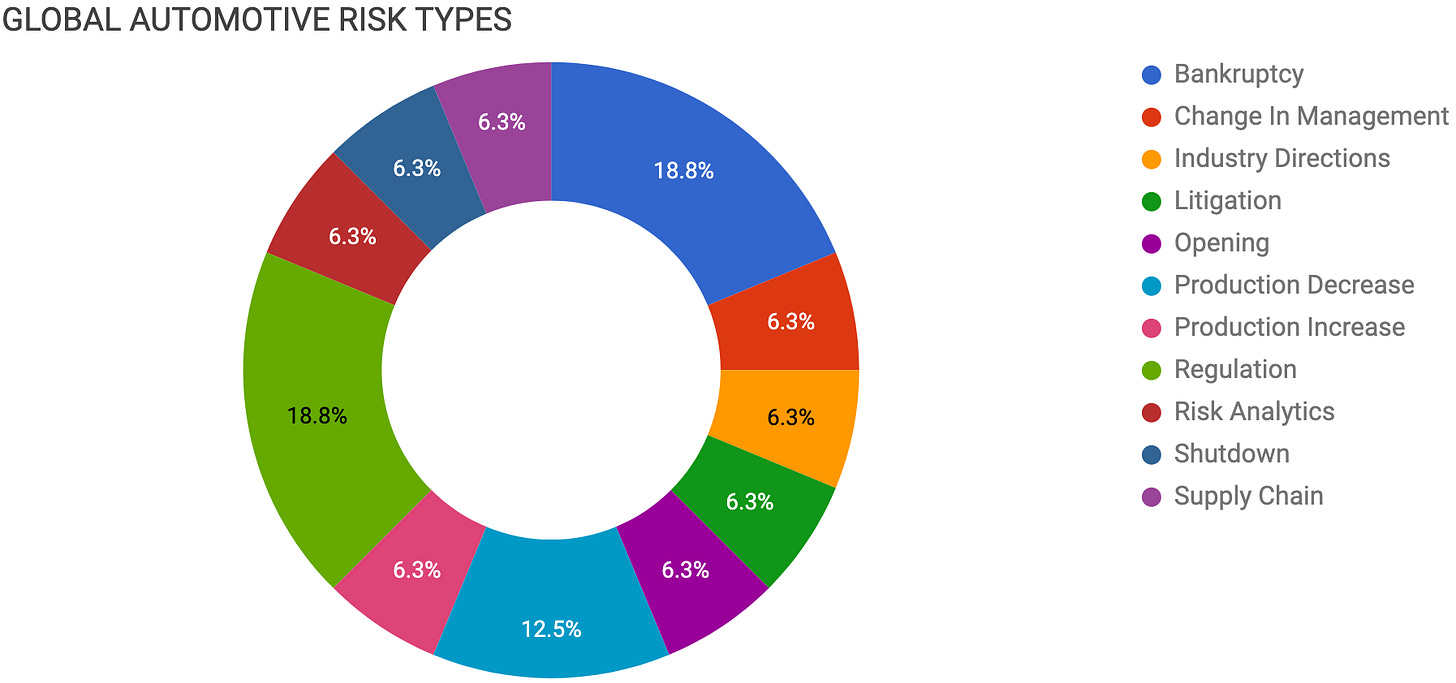
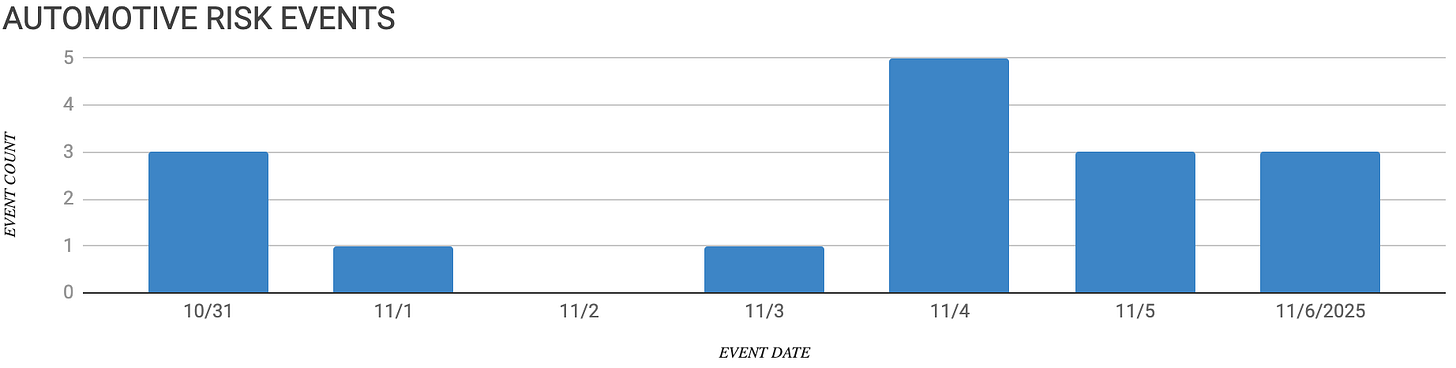
Contents
BANKRUPTCY
First Brands’ German units file insolvency
Exro collapses amid cash flow crisis
Lithion pauses EV battery recycling plant
CHANGE IN MANAGEMENT
Wingtech appoints Sophie Shen president
INDUSTRY DIRECTIONS
Tesla approves $1T Elon Musk package
LITIGATION
First Brands sues founder over fraud
OPENING
Vianode to build Ontario graphite plant
PRODUCTION DECREASE
Nissan cuts Rogue output over chip shortage
Nissan slashes Smyrna production after aluminum fire
PRODUCTION INCREASE
Novelis to restart Oswego aluminum plant early
REGULATION
Trump order expands auto parts tariff relief
New US port fees raise automaker costs
Canada disputes Stellantis Jeep production shift
RISK ANALYTICS
Rising costs dominate auto logistics survey
SHUTDOWN
Honda halts Celaya plant amid chip crisis
SUPPLY CHAIN
Nexperia halts China shipments over governance breach
Bankruptcy
Two German subsidiaries of US auto parts supplier First Brands Group, Diepersdorf Plastic Manufacturing and Linden Plastics Manufacturing GmbH, have filed for insolvency after the parent company’s Chapter 11 filing in September. The two firms make radiator grilles, mirror caps, and steering wheel covers for European automakers.
Falling production volumes and heavy debt pushed them into crisis, putting about 1k jobs at risk. Germany’s insolvency program will cover wages for two months while talks continue with automakers and suppliers.
Exro Technologies, a Canadian clean-tech firm that partnered with Stellantis on EV motor control systems for Dodge, Chrysler, and Jeep, has filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy. The filing covers its US units, Exro Vehicle Systems, and SEA Electric.
Despite promising technology, Exro struggled with mounting losses and cash flow shortages, ultimately leading to liquidation and delisting from public markets. The collapse highlights the vulnerability of smaller EV tech firms in a tightening investment climate.
Lithion Technologies has filed for creditor protection in Canada, pausing operations at its $28.3M EV battery recycling plant in Saint-Bruno. Despite receiving more than $70M in funding from GM Ventures and Investissement Québec, the company ran out of cash amid a cooling EV battery market. The shutdown forces Call2Recycle’s national battery recovery program to ship materials to US processors at a higher cost.
Change In Management
Wingtech Technology has promoted Columbia Law graduate and general counsel Sophie Shen Xinjia to president as it works to resolve its standoff with the Dutch government over chipmaker Nexperia.
The Netherlands seized Nexperia in September under a national security law, prompting China to block chip exports from its Dongguan plant, which produces about 70% of its output.
Shen, formerly with Bosch and TRW Automotive, brings cross-border legal experience as Wingtech navigates sanctions and governance hurdles.
Editor’s note: The story continues to unfold in the Supply Chain section below. We also did a deep dive on the Nexperia chip crisis in last week’s Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #454.
Industry Directions
Tesla shareholders have approved a record compensation plan for Elon Musk, potentially worth up to $1T.
The payout depends on the company meeting aggressive targets, including 12M annual vehicle sales and 1M robotaxis by 2035.
The plan underscores investor confidence in Tesla’s long-term dominance in EVs and autonomy, while raising the bar for growth expectations across the industry.
Litigation
First Brands’ new leadership accused founder Patrick James of diverting company funds to luxury assets and falsifying billions in financing before its bankruptcy.
The fraud claims in the lawsuit exacerbate the crisis at First Brands, raising concerns about governance failures and financial transparency across complex supplier networks that are critical to automakers.
Opening
Norway’s Vianode plans to invest over $1.4B in a large-scale synthetic graphite plant in St. Thomas, Ontario, near PowerCo’s upcoming battery site. The “Via Two” project is scheduled to begin production in 2028 and is expected to reach an annual capacity of 150k tonnes, employing approximately 1k people.
Vianode has already signed a supply deal with GM, positioning the plant as a key North American source of battery-grade graphite and aiming to reduce reliance on China.
Production Decrease
Nissan will cut production of its Rogue/X-Trail SUV by about 900 units next week at its Kyushu plant in Japan due to a shortage of Nexperia semiconductors, according to an internal source. Nissan said it will make “small-scale production adjustments” at both Kyushu and Oppama plants while monitoring developments.
Nissan also reduced October production at its Smyrna, Tennessee, plant by approximately 7.4k vehicles due to shortages of aluminum and electronic components. The downtime, including full-line stoppages on October 24 and 27, followed a fire at Novelis’ Oswego, New York mill, which disrupted aluminum supply to Nissan, Ford, and Stellantis.
Nissan is securing alternative materials and prioritizing production of the Murano, Pathfinder, and Infiniti QX60 through November. Executives also warned that the ongoing Nexperia chip dispute could add further instability. The overlapping material and chip shortages continue to pressure its North American production schedules.
Production Increase
Novelis will restart that same Oswego, New York, aluminum plant in December, ahead of schedule. The company had initially targeted early 2026 for reopening, but accelerated the repairs by installing new roof trusses and securing all 7k replacement parts.
CEO Steve Fisher said the restart will restore key capacity while the company absorbs a $550M to $650M cash flow impact, mostly covered by insurance. The early restart is expected to ease aluminum shortages that have constrained North American vehicle production.
Regulation
President Trump’s October 17 executive order expands the list of auto parts eligible for lower industry-specific tariffs.
Automakers can now classify more imported components, such as touchscreens, drive axles, and ECUs, under a 25% duty instead of higher steel or reciprocal tariffs. The change allows importers to self-certify parts for automotive use, reducing costs that previously reached up to 50% for some materials.
Automakers from the EU, Japan, and soon South Korea will benefit from reduced rates of around 15%, while USMCA-compliant parts remain mostly exempt. GM expects lower tariff exposure this year, estimating $3.5B to $4.5B.
The policy offers short-term relief and greater cost predictability amid persistent US trade friction and high material prices.
Global car carrier Wallenius Wilhelmsen says automakers shipping vehicles to the US could face an extra $200 to $300 per unit after new US port fees on Chinese and other foreign-built ships took effect in mid-October.
The US Maritime Administration introduced the fees as part of trade-related measures targeting foreign-built vessels amid ongoing tensions between the US and China.
The company expects to incur up to $100M in additional costs this quarter, which will be passed on to customers. Higher port charges could squeeze automaker margins and disrupt delivery schedules.
The Canadian government has launched a formal dispute against Stellantis after the automaker announced plans to move Jeep Compass production from Brampton, Ontario, to the United States.
Industry Minister Mélanie Joly called the decision “unacceptable” and confirmed a 30-day dispute process aimed at keeping production in Canada.
The move adds to growing US–Canada trade friction, coming on the heels of US tariffs on autos, steel, and aluminum, as well as Canada’s recent reduction to tariff-free import quotas for GM and Stellantis.
Risk Analytics
Rising costs top the list of challenges in the 2025 Automotive Inbound Logistics Survey. More than 40% of automakers and logistics providers say relentless jumps in freight, fuel, and labor costs are “crushing margins.” Trade wars and tariffs came in second, disrupting global sourcing and pricing.
About one in three also cited ongoing supply chain snags tied to geopolitics, material shortages, and the shift to EVs. The result: companies are renegotiating contracts, rethinking their sourcing strategies, and working to build more resilient inbound supply chains.
Shutdown
Honda stopped production at its Celaya, Mexico, plant due to chip shortages linked to Nexperia’s supply crisis. The Japanese Embassy in Mexico and AMIA confirmed the shutdown, with AMIA president Rogelio Garza warning that the shortage could spread across Mexico’s automotive sector if not resolved soon.
Supply Chain
Dutch chipmaker Nexperia has halted wafer shipments to its Chinese subsidiary after the local team refused to make payments and breached corporate governance rules.
The company accused staff in Dongguan of opening unauthorized accounts and misusing corporate seals, raising concerns over quality and IP security.
The move deepens Nexperia’s governance crisis following the Dutch government’s takeover of the company from its parent, Wingtech, in September.
China’s Commerce Ministry blamed the Netherlands for “turmoil and chaos” in the global chip supply chain.
Nexperia is now seeking alternative sources to maintain a steady supply to Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz.