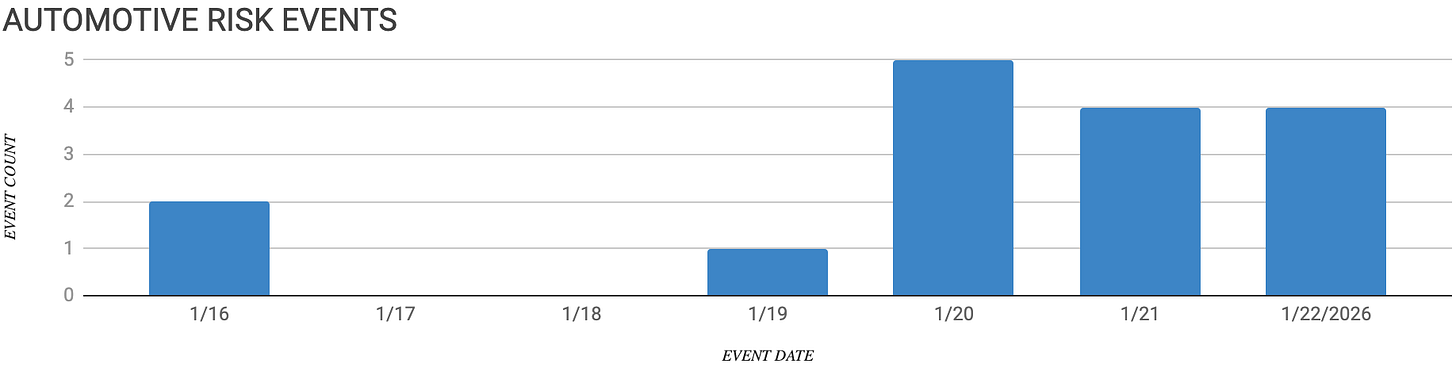
Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #466
January 16 - 22, 2026, by Elm Analytics
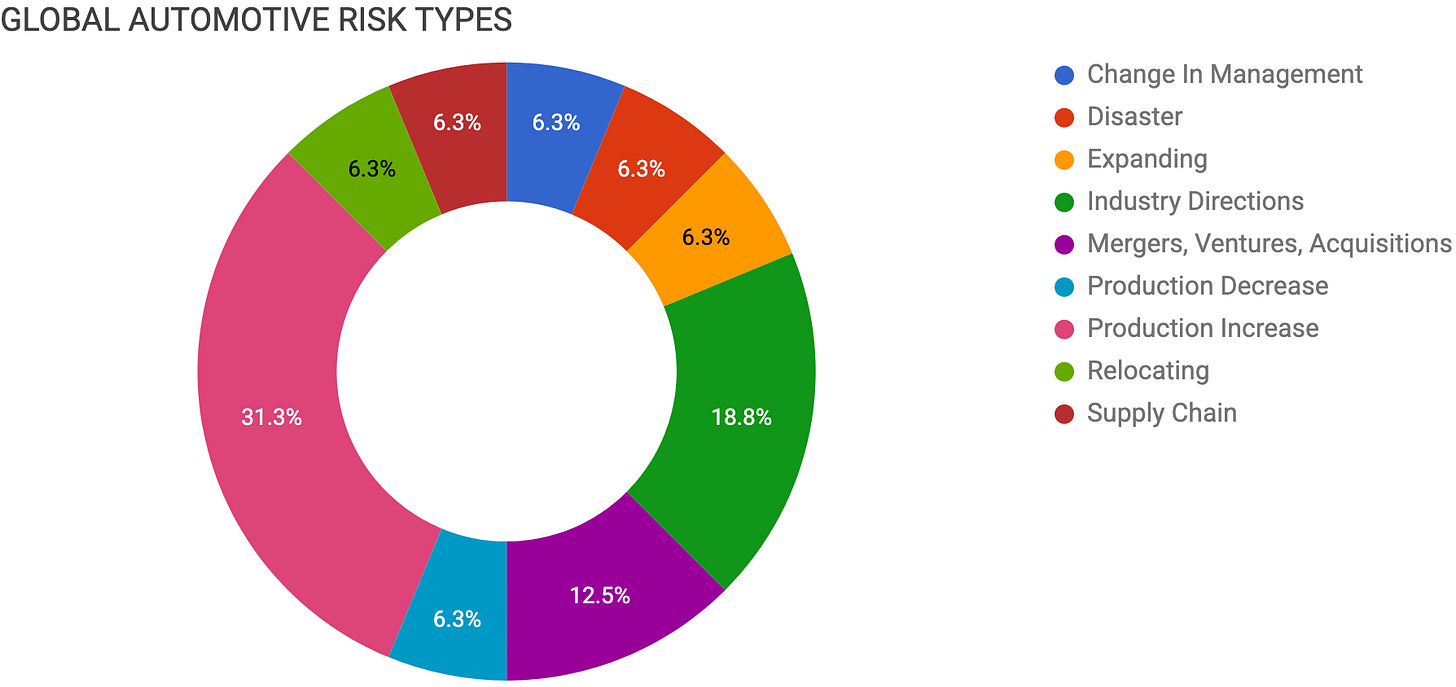
Contents
CHANGE IN MANAGEMENT
Mitsubishi names new president, COO
DISASTER
Winter storm threatens southern US auto supply
EXPANDING
Delta Tecnic expands Querétaro wiring capacity
INDUSTRY DIRECTIONS
Supplier sentiment up, outlook pessimistic
Slovakia leads cars per capita
S&P Global 2026 Supplier Outlook
MERGERS, VENTURES, ACQUISITIONS
Renault reintegrates Ampere EV unit
PwC sees steady rising auto M&A
PRODUCTION DECREASE
Honda, GM end fuel cell venture
PRODUCTION INCREASE
Geely targets 6.5M global sales
Rivian builds R2 validation units
Mercedes starts electric GLB Hungary
BMW keeps US BEV launch plan
Dongfeng launches giant die casting plant
RELOCATING
GM shifts Buick Envision China → Kansas
SUPPLY CHAIN
Looming: AI data centers squeeze auto DRAM
Change In Management
Mitsubishi Motors will name Keisuke Kishiura president and COO on April 1, with Takao Kato moving to the chairman and CEO role, as it seeks to address weaker performance and partnership execution.
The company is facing sales declines in Southeast Asia, an interim net loss, an 81% drop in operating profit, and US tariff headwinds because it imports all vehicles from Japan.
Mitsubishi is discussing access to Honda and Nissan local factories, a move that could reshape its manufacturing footprint and supplier mix.
Disaster
The Winter Storm Fern is likely to slow or shut down some automotive suppliers across the Southeastern US. Ice-driven outages, road closures, and staffing gaps can trigger short stops at just-in-time plants.
Sites in Texas, Arkansas, Tennessee, the Carolinas, Georgia, and Virginia look most exposed because they depend on road corridors in the storm path.
If disruptions last more than a few days, southern freight failures could cascade into meaningful production and revenue hits for OEMs and Tier-1s.
Expanding
Delta Tecnic is expanding in Querétaro, Mexico, with an $11.5M investment to add capacity for automotive wiring components, supporting its nearshoring push.
Industry Directions
Supplier sentiment improved in Q4 2025, with 60% rating their own performance as excellent or good, driven by stronger demand and improved supply chain resilience.
But the six-month outlook for the broader industry stayed pessimistic as tariffs, input costs, and regulatory uncertainty squeezed margins and limited pricing leverage.
Financial distress remains a key risk signal: most respondents are concerned, and more expect conditions to worsen.
Slovakia is the world’s top carmaker per capita, building almost 1M vehicles a year with a population of 5.4M.
Since 1989, Kia, Volkswagen, Stellantis, and Jaguar Land Rover have scaled up there, drawn by lower labor costs, strong productivity, a central location, and a supplier base of about 360 firms.
Low-carbon power and incentives also help, including Kia’s $32M tax credit for a $118M EV line upgrade, while the industry supports jobs and training pipelines in the Zilina region.
Mergers, Ventures, Acquisitions
Renault plans to close Ampere Holding and fold its EV and software work back into the group to streamline the organisation, cut costs, and speed up future projects.
The plan was presented to trade unions and is due to take effect on July 1, with most employees’ jobs and contracts expected to stay in place.
Ampere, launched in late 2023 with an IPO plan that was later put on hold, now reports to Renault Group CTO Philippe Brunet and is expected to serve as Renault’s advanced engineering centre for EVs and software.
Ampere’s Electricity division factories in northern France and its engine plant are set to return to direct Renault control.
It is the second major restructuring in under two months under CEO François Provost, following the December move to close Mobilize’s car-sharing services and reintegrate its energy and data activities.
PwC expects auto M&A to stay steady or rise in 2026 as suppliers face inflation, lower volumes, and shifting tariffs.
Those pressures are driving consolidation and vertical integration, with suppliers selling non-core assets, raising cash, and tightening spend on capacity and electrification.
PwC also flags AI-driven analytics as a growing factor in deal valuation and integration, which could speed deal cycles and accelerate supply chain changeovers.
Production Decrease
Honda and GM plan to stop producing their joint fuel-cell battery system in Michigan in 2026, ending a partnership that began in 2017.
Production began in January 2024 to support Honda’s fuel cell vehicle work in Ohio, but both companies now cite low demand and slower growth in the hydrogen market.
GM has also shifted focus away from hydrogen research toward EVs, batteries, and charging, while Honda is reallocating as well.
Production Increase
Geely is targeting more than 6.5M global vehicle sales by 2030 and aiming for a top-five spot, with about one-third of sales expected to come from overseas by decade’s end.
It plans new energy vehicle platforms across A to E class models to shorten R&D cycles and cut per-model production costs by more than 30%, while deepening partnerships such as Renault.
For suppliers, that usually means larger-volume requests, faster RFQs, and tighter cost and delivery targets as Geely expands in Southeast Asia and Latin America.
Rivian has started building R2 validation units on its Normal, Illinois line, after completing the R2 factory in just 12 months.
The pre-production builds are a key step toward H1 2026 deliveries. They stress-test parts fit, supplier consistency, and build quality before the production ramp.
Mercedes has started producing the electric GLB in Kecskemét, Hungary, after moving production from Mexico and adding local battery-pack assembly to cut logistics costs and time.
It also plans to shift some C-Class production to Hungary in 2026, citing costs there that are less than half Germany’s.
The footprint shift supports margin protection and lowers tariff exposure as US tariffs and China competition pressure profitability.
BMW still plans to start BEV production in Spartanburg in late 2026, even after AESC paused construction of its South Carolina cell plant in June 2025.
Until the Woodruff battery assembly plant and local cell output are ready, AESC will supply cells from its global network. That reduces launch-delay risk, but it increases tariff and geopolitical exposure if cells are imported.
Dongfeng has launched a Wuhan die-casting plant with the industry’s largest 16k-ton and 10k-ton lines, with mass production expected in April.
The site will make integrated NEV structural parts such as battery casings and trays, initially for models including the eπ 007, eπ 008, and Voyah Dreamer.
Relocating
GM will shift next-generation Buick Envision production for North America from China to Fairfax Assembly in Kansas City, Kansas, in 2028. That will push a supplier and logistics reset toward US content as Fairfax moves from a limited Bolt EV run to higher-volume ICE SUV output.
Supply Chain
Automakers are bracing for a new semiconductor squeeze as AI data center growth tightens DRAM supply.
Some suppliers are already seeing memory chip prices rise by more than 100%, and UBS warns disruptions could start in Q2.
Even though automotive uses less advanced memory than AI servers, both compete for upstream inputs like silicon wafers, and DRAM makers are prioritising higher-margin data center demand.
S&P Global Mobility warns the window is narrowing to redesign electronics and lock in supply, with ADAS-heavy vehicles and electronics-focused suppliers most exposed.
If DRAM tightens further, module shortages could quickly spill into production stoppages, echoing a smaller version of the pandemic-era chip crunch as vehicle electronics content keeps rising.








Couldn't agree more. Your continuous tracking of these supply chain dynamics, especially with AI's looming impact on DRAM, is always so insightful.