Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #465
January 9 - 15, 2026, by Elm Analytics
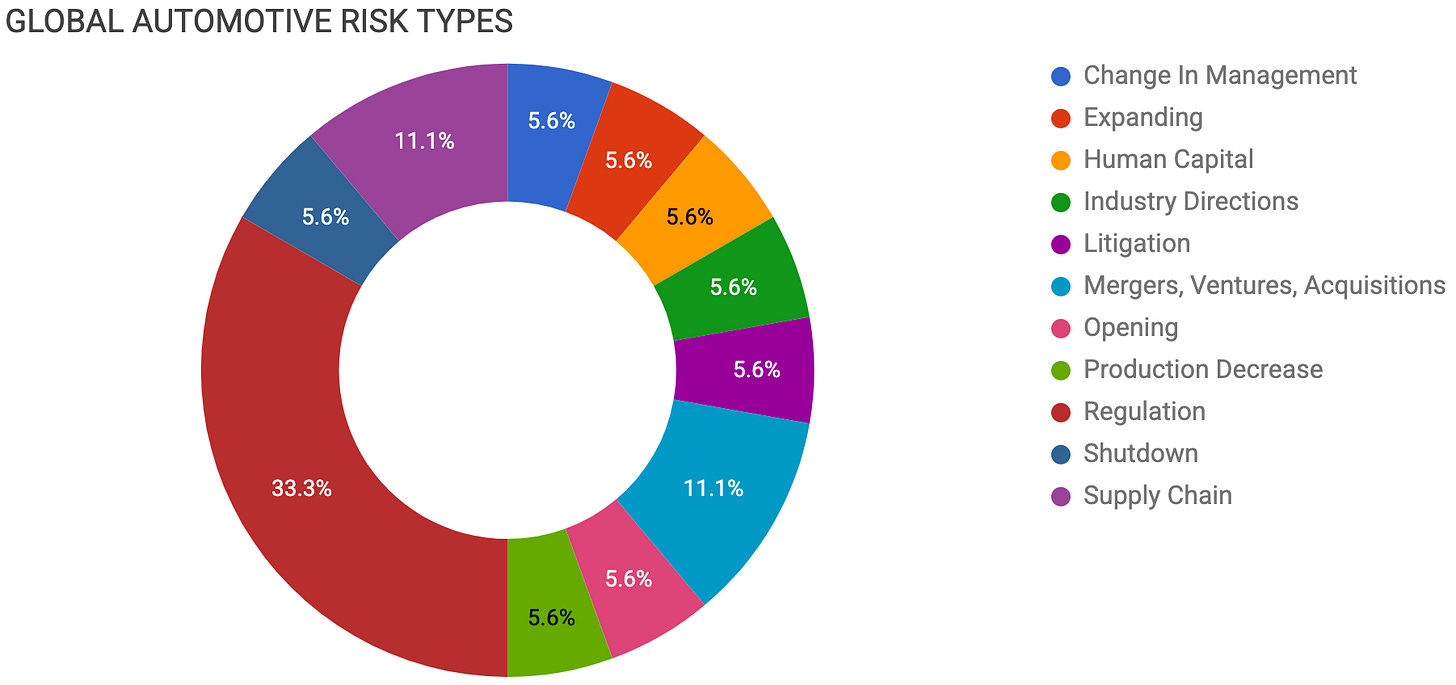
Contents
CHANGE IN MANAGEMENT
Lucid overhauls software leadership, OTA push
EXPANDING
ZF expands EV axle production Hungary
HUMAN CAPITAL
ZKW to cut 600 Austria jobs
INDUSTRY DIRECTIONS
Dark factories advance toward full automation
LITIGATION
Dutch court weighs Nexperia governance probe
MERGERS, VENTURES, ACQUISITIONS
Ford explores BYD battery supply deal
Italy approves FountainVest EuroGroup acquisition
OPENING
SL MEX opens Mexico lighting plant
PRODUCTION DECREASE
Stellantis ending North America PHEV production
REGULATION
USMCA 2026 review drives North America uncertainty
EU & China agree EV price framework
SHUTDOWN
Volvo pauses Novo Energy battery project
SUPPLY CHAIN
Maersk Red Sea test highlights risk
Wingtech localizes Nexperia China supply
Change In Management
Lucid is overhauling its software leadership and pushing OTA fixes after a viral critique exposed persistent quality and system reliability issues. The response comes amid executive turnover and heavy program load, including new vehicle launches and Saudi production ramp-up.
Expanding
ZF Chassis Modules is investing about $30M in Debrecen, Hungary, to expand production of front and rear axles for electric vehicles built at BMW’s nearby plant, creating 230 new jobs.
Human Capital
ZKW will eliminate 600 jobs in Lower Austria by the end of 2027, mostly at Wieselburg, as part of a 2.3k position global reduction tied to restructuring.
Industry Directions
Dark-factory automotive assembly is moving from concept to early deployment, with China already running highly automated EV lines that operate 24/7 with minimal on-site labor and dimmed lights, and Western OEMs and suppliers retrofitting existing lines to close the gap.
Analysts now expect the first truly fully automated car assembly line to be in production by around 2030, likely at a US or Chinese automaker. In these plants, humanoid and specialized robots will handle the remaining manual tasks. Intricate parts such as wiring harnesses and interiors will be redesigned to enable automation.
Meanwhile, the broader “dark factories” market for highly automated plants is projected to grow rapidly through the 2020s, as OEMs and Tier 1s pursue labor savings, faster model changeovers, and greater supply chain resilience.
Litigation
Nexperia was back in an Amsterdam courtroom earlier this week as judges weighed whether to launch a formal probe into alleged mismanagement tied to its Chinese owner, Wingtech.
Earlier clashes over control triggered export disruptions and chip shortages, reminding automakers how quickly political tensions around a single supplier can disrupt global production.
Wingtech says Nexperia’s Dutch team has blocked its integration plans and restricted wafer flows, harming the broader group’s manufacturing.
Nexperia’s European leaders say the real problem is risky, opaque moves on the Chinese side that threatened the company’s stability and have led to steps such as suspending the CEO and parking Wingtech’s shares with a court‑appointed custodian.
For carmakers, the ongoing tug of war keeps a key chip source looking fragile, raising the risk of renewed export freezes, sudden allocation cuts, or last‑minute re‑sourcing if governance flares up again.
The court will now decide whether to open a full investigation and possibly tighten interim controls, with a written decision expected in the coming weeks that will be closely watched across the auto supply base.
Mergers, Ventures, Acquisitions
Ford is reportedly discussing a battery supply deal with BYD to address tightening battery supply options for its expanding hybrid lineup, as electric vehicle demand cools.
The potential deal would involve importing BYD batteries to Ford plants outside the US, heightening dependence on Chinese capacity and raising geopolitical risk in powertrain sourcing.
Italy approved Chinese private equity firm FountainVest’s purchase of a major stake in EuroGroup Laminations. The approval was granted under golden power rules.
The decision allows the EV motor component supplier to be taken private in 2026. The deal includes unspecified conditions. The approval follows a steep drop in EuroGroup’s valuation, caused by slower EV momentum and supply chain strain.
Opening
South Korea’s SL MEX has opened a new automotive lighting module plant in San Luis Potosi, Mexico, investing $44M and adding more than 500 jobs to support global OEMs including BMW, GM, Kia, and Hyundai. The facility has capacity for up to 1M lighting modules annually and is designed to scale production as demand grows.
Production Decrease
Stellantis will end all North American PHEV production in 2026, eliminating Jeep 4xe and Pacifica PHEV models despite strong prior demand. This decision follows recalls and shifts the company's focus to other electrified powertrains. Suppliers that depend on PHEV volumes may face immediate demand losses, driving supply chain consolidation and contract renegotiation risks.
Regulation
Automakers face significant policy risk as the USMCA enters a high-stakes 2026 review. Political noise compounds uncertainty, sharply exposing companies that rely on North American integration for cost, sourcing, and capacity planning.
The mandatory July review forces the US, Canada, and Mexico to decide whether to renew the pact, withdraw, or take no action, fueling uncertainty about future trade rules.
President Trump’s sharp rhetoric signals he may threaten market access to extract concessions. In this environment, Canada’s auto sector is on hold, with automakers and suppliers facing risk on costs, sourcing, and production plans until the framework becomes clear.
Industry leaders and key state policymakers are lobbying to preserve and refine the agreement, emphasizing its role in North American competitiveness with China and continued EV and supply chain investment.
Mexico heads into 2026 with strong domestic demand but weaker output and exports. USMCA uncertainty affects plant use and investment, with most vehicles sent to the U.S. Tighter rules or higher tariffs could quickly disrupt cross-border parts flows.
Taken together, the 2026 review has turned USMCA from a background assumption into a central strategic variable for North American automakers.
OEMs and suppliers must now develop scenario plans addressing multiple possible trade and regulatory outcomes, identifying operational, sourcing, and investment implications under each scenario, while hoping policymakers ultimately choose continuity over disruption.
Over the past week, the EU and China agreed on a framework for “price undertakings” that would let Chinese EV makers avoid some or all EU anti-subsidy tariffs by accepting minimum prices and volume limits on exports.
The European Commission issued detailed guidance on how companies can submit these undertakings, with approvals to be decided on a case-by-case basis and conditioned on offsetting the subsidy advantage.
Now, individual firms must assess whether to participate by evaluating the terms set by the Commission and deciding if accepting minimum prices and volume caps is preferable to continuing to pay existing duties of up to 35.3% above the standard 10% car tariff.
Both sides present this as a breakthrough or “soft landing.” However, the dispute is not fully resolved, as each company must make its own decision.
Analysts expect fewer ultra-cheap Chinese EVs but higher margins and potentially higher consumer prices in Europe, while political scrutiny inside the EU over minimum-price mechanisms is likely to continue.
Shutdown
Volvo Cars has halted its Novo Energy battery project after costs rose and the search for a new partner failed following Northvolt's bankruptcy. The last 75 jobs are being cut.
Management says they are still talking with battery makers, but EU financial support is needed to restart the project. Delays in building battery capacity in Europe have created sourcing risks for automakers planning future electric vehicle production in the region.
Supply Chain
Last week, Wingtech said Nexperia China is choosing local silicon wafer suppliers and expanding domestic packaging to stabilize production. While the local sourcing pivot may reduce near-term supply risk in China, it will likely deepen global supply fragmentation for automakers.
Maersk’s cautious Red Sea test transit signals progress but leaves automotive logistics exposed to continued delays and cost risk.