Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #437
June 13 - 19, 2025, by Elm Analytics
Editor’s Note
At last week’s AIAG Supply Chain Conference, one message stood out: uncertainty is paralyzing progress.
Elm Analytics’ Chief Commercial Officer, Sig Huber, joined the Auto Supply Chain Prophets Podcast to break down why delayed investment, conflicting policy signals, and unpredictable demand are creating a dangerous freeze in decision-making.
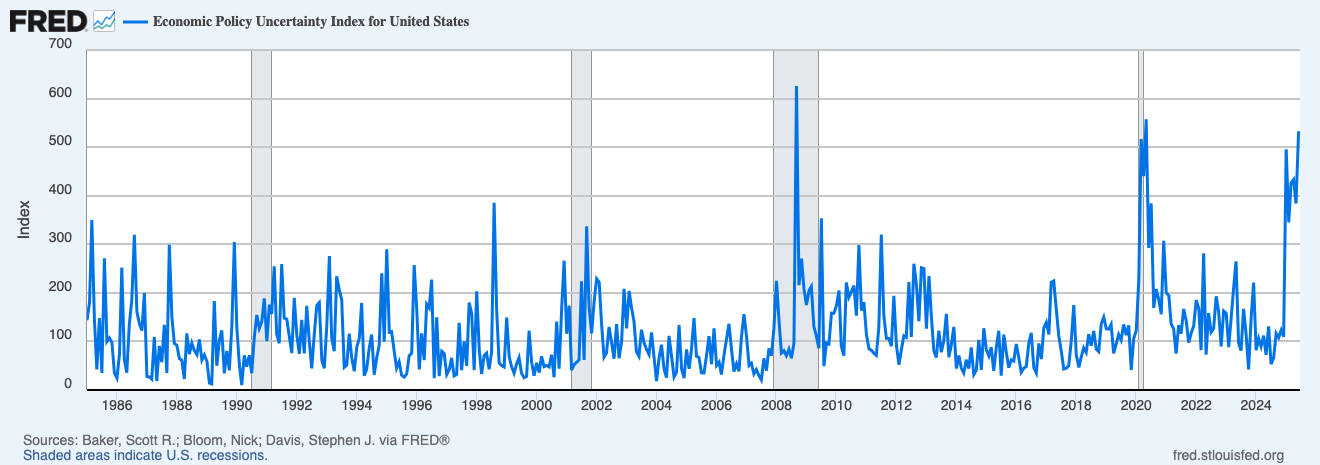
It’s not just a feeling. The data backs it up: The Economic Policy Uncertainty Index, tracked by the St. Louis Fed, has surged to levels not seen since the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic.
🎧 The full episode just dropped. It’s a must-listen for anyone watching risk in the automotive supply chain.
Nick Gaydos
Contents
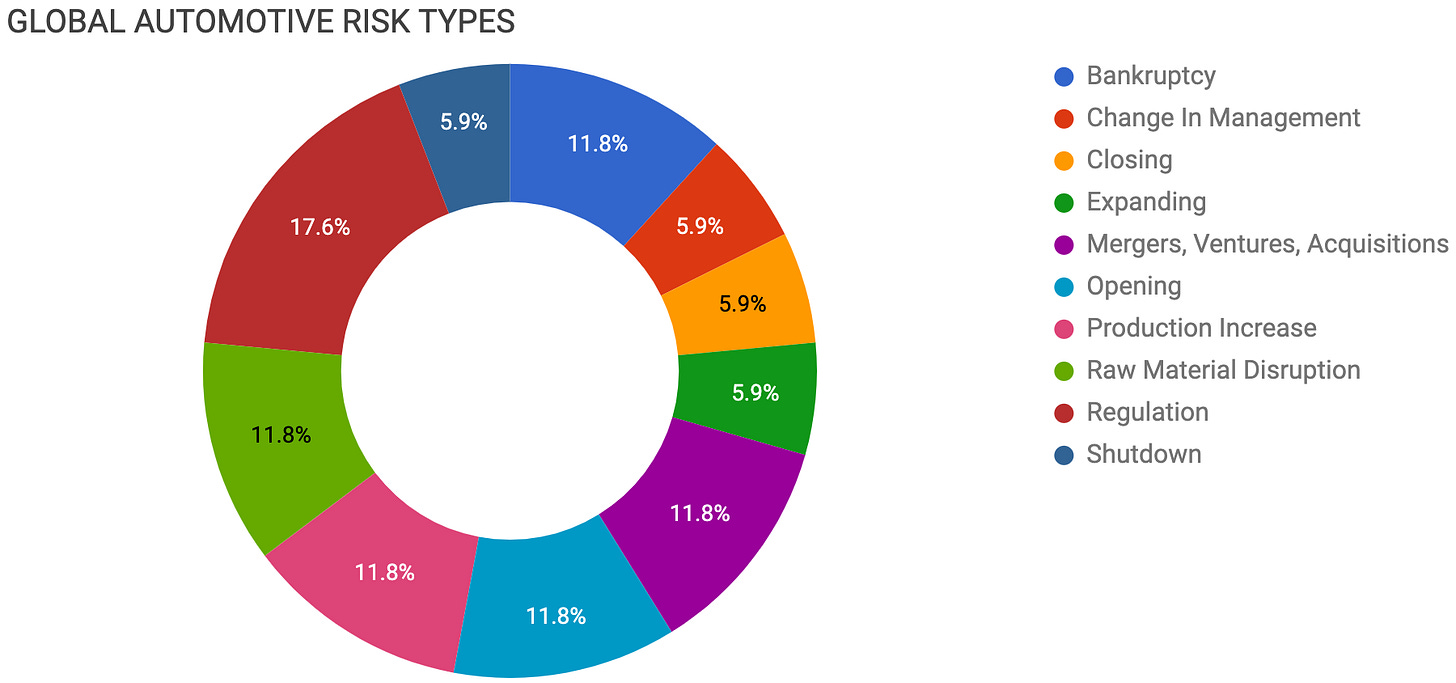
BANKRUPTCY
Marelli collapse underscores supplier fragility
LeddarTech bankruptcy signals niche tech risk
CHANGE IN MANAGEMENT
Renault seeks CEO amid EV pressure
CLOSING
Michelin closing Querétaro plant in 2025
EXPANDING
Xiaomi expands EV output in Beijing
MERGERS, VENTURES, ACQUISITIONS
Nippon Steel acquires US Steel
Adani, CATL eye India battery plant
OPENING
Electra restarts cobalt refinery project
Zoox opens major robotaxi facility
PRODUCTION INCREASE
Toyota boosts hybrid battery production
Chinese automakers grow European footprint
RAW MATERIAL DISRUPTION
Antimony curbs squeeze battery makers
Rare earth limits hit EV supply
REGULATION
China EV surge stirs Brazil backlash
Ford battery plant faces IRA risks
Japan-US tariff talks stall again
SHUTDOWN
Tesla pauses Model Y, Cybertruck lines
Bankruptcy
Marelli’s collapse last week illustrates the mounting financial strain on automotive suppliers, as tariffs compound pressures from high debt, rising rates, and underwhelming EV returns.
Global suppliers with import exposure face growing insolvency risk, and 69% of suppliers say tariffs have hurt competitiveness, according to MEMA.
Lower-tier firms are especially vulnerable, prompting urgent demands for faster OEM payments and tariff cost-sharing. As trade policies shift, structural instability is deepening across key supply chain tiers.
Quebec-based ADAS supplier LeddarTech will file for bankruptcy after failing to secure funding or a buyer. Originally a lidar maker with a sizable patent portfolio, it defaulted on bridge financing and will cease operations.
Its Nasdaq listing is set for delisting, board members will resign, and investor recoveries are expected to be minimal. The collapse highlights the fragility of niche tech firms in capital-intensive segments.
Change In Management
Renault is seeking a new CEO after Luca de Meo’s abrupt exit to lead luxury group Kering, raising concerns over the automaker’s direction amid rising Chinese competition and supply chain pressures.
Internal candidate Denis Le Vot and Stellantis executive Maxime Picat are reportedly seen as top contenders. De Meo’s departure adds leadership uncertainty as Renault navigates electrification and scale constraints.
Closing
Michelin will shutter its Querétaro, Mexico, plant in 2025, consolidating production in León amid demand changes and outdated manufacturing lines.
Expanding
Xiaomi is expanding EV production with a new $88M Beijing land lease, one of the few OEMs greenlit to grow amid industry overcapacity. Surging demand for its SU7 and upcoming YU7 has driven it to raise its 2025 delivery targets.
Mergers, Ventures, Acquisitions
Nippon Steel has finalized its acquisition of US Steel under a security agreement, giving the US government veto power over key decisions to protect critical capacity.
As a major flat-rolled steel supplier for vehicle bodies and EV components, US Steel’s new ownership could reshape North American sourcing. Nippon’s $11B investment aims to boost domestic capacity and reduce offshore dependence, though labor stability remains a concern amid union pushback.
Adani and CATL are discussing establishing a battery cell manufacturing facility in India. Their focus will be on producing lithium iron phosphate and sodium-ion batteries.
Opening
Electra Battery Materials will begin $750k in site prep this summer to restart construction on its cobalt sulfate refinery in Ontario, which has been stalled since 2023.
Backed by $54M in funding from a strategic investor and the US and Canadian governments, the project is $6M short of completion.
Once operational, it would be North America’s only battery-grade cobalt refinery, with 80% of its capacity contracted to LG Energy.
Amazon-owned Zoox has opened a 220k ft² robotaxi plant in Hayward, California, marking its shift from development to manufacturing. The facility will integrate, assemble, and test up to 10k custom autonomous vehicles annually, starting with deployments in Las Vegas and San Francisco and later expanding to Austin and Miami.
Production Increase
Toyota is adding battery pack assembly lines to its Ontario plants ahead of 2026 RAV4 hybrid and plug-in hybrid production. Modules will come from its North Carolina facility, marking a step toward vertical integration.
Despite new US auto tariffs, Toyota plans to maintain output in Canada, citing a long-term investment strategy. The move strengthens regional hybrid supply amid growing trade friction and EV supply chain realignment.
Despite EU tariffs of up to 35%, Chinese automakers like BYD and Geely are gaining ground in Europe by pushing hybrids and gasoline cars exempt from the levies and targeting markets like Italy and Spain.
In April, Chinese EV sales jumped 59% year-over-year and surpassed Tesla, even though two-thirds of the sales weren’t fully electric.
Dealers credit China’s rapid six-month design cycles, while factories in Hungary and Turkey aim to bypass future tariffs. The workaround, however, risks undermining EU climate goals by fueling combustion engine imports.
Raw Material Disruption
China’s export restrictions on antimony have disrupted the automotive lead-acid battery supply chain, pushing prices above $60k per metric ton and squeezing OEM and supplier margins.
Lead-acid batteries are used in internal combustion and hybrid vehicles for starting and low-voltage systems, which depend on high-purity antimony-lead alloys that are difficult to source outside China.
Automakers and suppliers, including Clarios and GS Yuasa, are passing rising costs down the chain. While recycling offers partial relief, the shortage threatens production continuity and exposes a critical vulnerability in ICE and hybrid platforms.
While antimony restrictions were put into place in 2024, China has recently tightened its export controls on additional rare earth minerals, prompting automakers like Mercedes and Porsche to seek new suppliers $.
They are turning to companies such as Rainbow Rare Earths in South Africa to reduce the risk of magnet shortages that could affect EV production.
Even with temporary relief from licensing in Beijing, most magnet manufacturing is still concentrated in Asia. Additionally, ongoing shipping delays reveal weaknesses in the supply chain.
Regulation
Led by BYD, Chinese automakers have rapidly expanded EV exports to Brazil, with over 22,000 EVs in early 2025, taking advantage of low tariffs and import quotas.
With Chinese brands now controlling 80% of Brazil’s EV market, local industry groups are urging the government to fast-track a tariff hike to 35%. The groups are concerned that the excess imports are slowing investments in Brazil (BYD’s Bahia factory faces delays until late 2026).
Ford’s $2.5B BlueOval Battery Park in Michigan, central to its low-cost LFP battery strategy using CATL technology, is under threat of losing IRA subsidies due to political and competitive pushback. A House budget bill targets the plant’s Chinese licensing ties, potentially putting 1.7k jobs at risk.
Sources reportedly point to GM’s lobbying as a key factor, as it promotes a non-China supply chain built with South Korean partners.
Despite mounting political headwinds, Ford defends its CATL alliance as the most cost-effective option. The dispute highlights competing paths to EV battery leadership amid rising pressure to localize and de-risk US supply chains.
Japanese Prime Minister Ishiba and US President Trump failed to reach a deal on US auto tariffs during their June 16 summit, leaving a 25% levy threat unresolved. While ministerial talks will continue, key differences persist, with Ishiba insisting any agreement must safeguard Japan’s auto industry.
The US has granted a 90d tariff reprieve, but its extension is uncertain. Japan points to its automakers’ 3.28M annual US vehicle output to argue against the duties. The stalemate prolongs uncertainty and risks disruption in Japan’s largest export market.
Shutdown
Tesla will shut down Model Y and Cybertruck production for the week of July 4 to perform line maintenance at its Austin Gigafactory, marking the third such pause in a year. The slowdown reflects changing production dynamics and comes as Tesla prepares to launch a pilot robotaxi service in Austin.