Automotive Supply Chain Risk Digest #356
December 1 - 7, 2023, by Elm Analytics
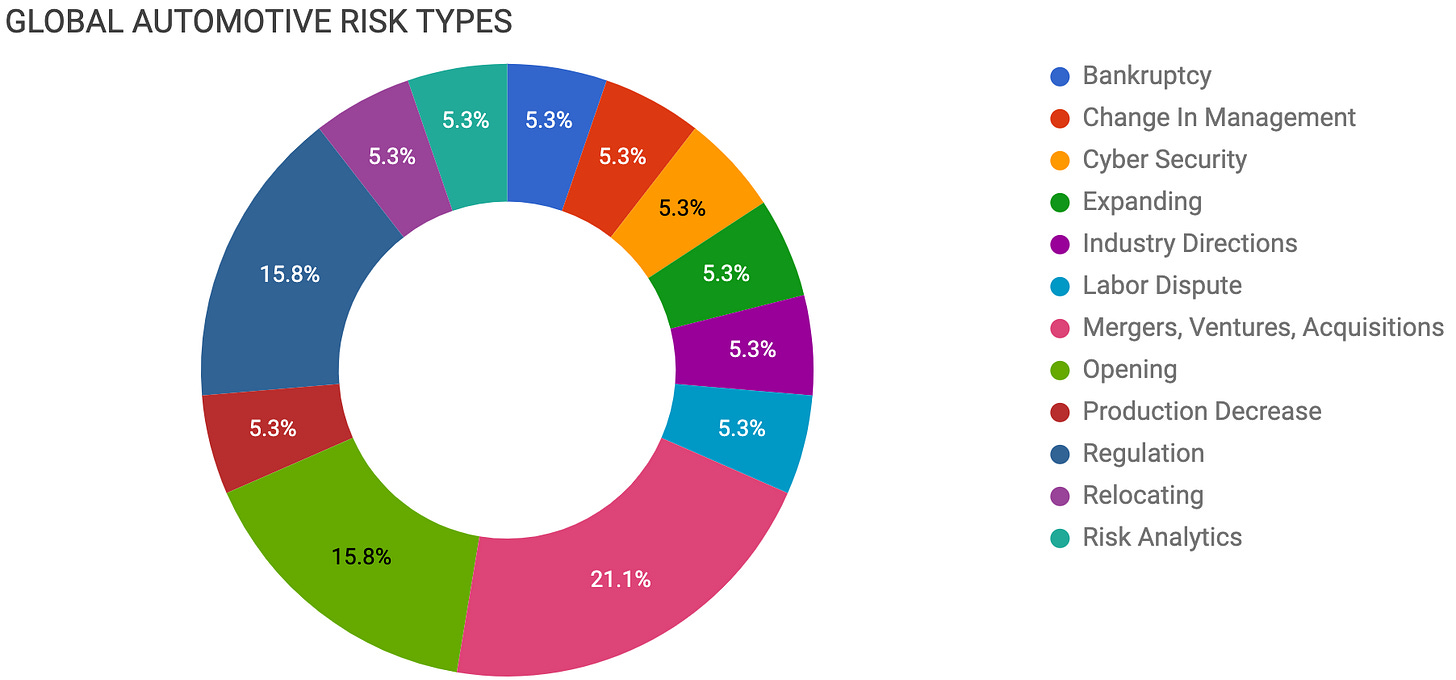
Bankruptcy
Quality Team 1, a Detroit, Michigan, vendor to Magna and other automotive suppliers, has filed for bankruptcy $ with over $5M in liabilities and $2M in assets.
The company, specializing in quality management, launch support, and warehousing, petitioned for bankruptcy protection under Subchapter V of Chapter 11, indicating an intention to continue operations. Its revenue fell to $15.4M in 2022, a 10% decline from the previous year.
This bankruptcy comes at a time when larger auto suppliers have managed financial pressures, but smaller suppliers further down the supply chain are facing mounting challenges.
Change In Management
Ganesh Venkataramanan, the lead of Tesla's Dojo project, has left the company after five years.
The Dojo supercomputer, integral to training machine learning models for Tesla's autonomous driving systems, is now led by a former Apple executive, Peter Bannon. Dojo is powered by a custom D1 chip designed by a team led by Venkataramanan and is considered a potential competitive edge for the company.
The departure of Venkataramanan, who was pivotal in setting up Tesla's AI hardware and silicon teams, and the exit of other team members pose challenges to this technologically advanced and expensive project.
Cyber Security
Yanfeng, a Chinese automotive supplier, has fallen victim to a cyberattack by the ransomware group Qilin. The attack, which initially disrupted production at Stellantis in November, has entered an extortion phase.
Qilin, known for breaching firms through phishing emails, has threatened to release "sensitive information" from Yanfeng. The impact of the cyberattack extended to General Motors, though it did not significantly disrupt their operations.
Cybersecurity experts highlight that such attacks can have far-reaching consequences, including potential breaches in customer networks and reputational risks. The attack against Yanfeng is part of a growing trend of ransomware attacks targeting manufacturers and other critical sectors.
The situation illustrates the increasing vulnerability of the automotive supply chain to cyber threats and the complex challenges in responding to and mitigating such attacks.
Expanding
Tesla is reportedly planning to restart the third phase expansion of its Shanghai, China plant project, potentially focusing on producing a $25k model. The project launched in 2021 but was suspended mid-2022, with team members reassigned to other departments. Shanghai's Giga factory, Tesla's most efficient production center globally, currently has a capacity of over 950k vehicles per year.
Industry Directions
BloombergNEF: Zero-Emission Vehicles Factbook: A special report prepared for COP28 (pdf)
Labor
Over 1k workers at Volkswagen's Chattanooga, Tennessee, factory have authorized a vote for representation by the UAW. The Chattanooga plant employs about 3.8k workers and manufactures the VW ID.4 EV and Atlas family of ICE SUVs. This potential unionization at the Chattanooga plant is the first test of the UAW's strategy to organize nonunion plants simultaneously.
Mergers, Ventures, Acquisitions
China's Nio will take over certain assets of two plants from its manufacturing partner, Anhui Jianghuai Automobile Group (JAC). The acquisition, valued at $442M, involves fixed assets and equipment at the F1 and F2 factories where Nio has produced its EVs.
The move, part of Nio's strategy to reduce manufacturing costs and increase independence in production, follows the company's addition to a Chinese industry ministry database allowing vehicle production.
China's state planner has been restricting the growth of production capacity in the auto industry and is reluctant to approve new players to join the overcrowded market. Regulators allowed Nio to produce and sell EVs in China via the collaboration with JAC in 2018, through which Nio paid JAC commission fees on each car it made.
Nio also announced plans to spin off its battery manufacturing unit to reduce costs and improve efficiency, with the spin-off involving seeking external investors and likely including a planned battery plant, testing equipment, and intellectual property.
Meanwhile, Huawei and JAC have jointly agreed to develop luxury EVs based on Huawei's smart car solutions. JAC will handle product development, while Huawei will exclusively handle global sales services for the models.
Startup EV Electra, based in Lebanon with offices in Canada and various European countries, acquired the electric luxury sedan project, the Emily GT, from National Electric Vehicle Sweden (NEVS). This acquisition also includes the PONS mobility ecosystem, an autonomous electric shuttle project. EV Electra plans to produce the Emily GT at the former Saab plant in Trollhättan, Sweden, its first entry into the EV market.
Opening
Symbio, a joint venture between Forvia, Michelin, and Stellantis, has inaugurated its first gigafactory named SymphonHy in Saint-Fons, France, touted as Europe's largest integrated production site for fuel cells. The factory currently has the capacity to produce 16k fuel cell systems annually, with plans to expand to 50,000 systems by 2026. The site encompasses Symbio's headquarters, R&D, and production facility.
Sila Nanotechnologies will expand its silicon anode materials facility in Moses Lake, Washington. The company will renovate the 600k sq ft facility, with initial production to begin in 2025. Mercedes-Benz will be one of the first commercial customers to use Sila's silicon anode in its G-Class series of EVs.
Indian steering and suspension systems manufacturer Rane Madras plans to invest $31M in opening its first plant in Aguascalientes, Mexico, to hire 300 workers.
Production Decrease
Stellantis has announced plans to reduce production shifts at two of its assembly plants in Toledo, Ohio, and Detroit, Michigan, potentially leading to thousands of job losses.
The decision, taking effect as early as February 5, is driven by the need to comply with California's stringent emissions regulations.
The Toledo plant, responsible for manufacturing the Jeep Wrangler and Gladiator, and one of the Detroit plants that produce the Jeep Grand Cherokee, will shift from three work shifts to two. This reduction is part of Stellantis's strategy to manage sales of these vehicles in line with state-specific emissions standards.
Although specific numbers were not provided, media reports suggest up to 1.2k employees could be laid off in Toledo. The Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act has been invoked, requiring a 60-day notice for mass layoffs. However, the number of affected employees might be less than the 500 threshold for a mass layoff.
Regulation
The Biden administration has implemented guidelines related to the $7.5k IRA tax credit that limits where EV manufacturers source battery materials. The regulations set a 25% ownership threshold for classification as a foreign entity of concern, which will apply to battery components in 2024 and expand to include critical battery raw materials in 2025. The rules aim to balance reducing dependence on Chinese materials with promoting EV adoption for climate goals and will have a public comment period before final implementation on January 1.
In the United States, the lengthy process for obtaining mining permits $, which can take up to 10 years, contrasts sharply with the two to three years required in countries like Canada and Australia. This delay poses challenges for automakers and suppliers eager to access critical materials for EV batteries. China's leg up in mining and processing essential EV battery materials, including graphite, complicates efforts to meet US EV tax incentives requirements.
While the Biden administration aims to foster a robust US EV supply chain and has released rules to reduce reliance on "foreign entities of concern" like China, industry groups stress the need for expedited domestic permitting to achieve electrification goals.
Ford and Rivian are among those urging the White House to streamline the review process for mining critical minerals. A September report from the Biden administration called on Congress to modernize the General Mining Act of 1872 and for federal agencies to update their processes to speed up permitting, maintaining high environmental and labor standards.
The EU will delay the implementation of local content rules that would have imposed tariffs on cars traded between the EU and Britain on January 1. The proposed three-year delay means British EVs with batteries made outside Europe will not face up to 10% tariffs.
This rule change is significant as Britain and the EU currently lack sufficient battery production capacity for the anticipated surge in EV production. The proposal still requires the support of EU governments but is expected to be welcomed by the auto industry.
Relocating
SKF will close its factory in Busan, Korea, with the complete shutdown expected in Q1-2024. The Busan factory, which employs about 90 employees and mainly produces automotive bearings, has struggled to penetrate the Korean domestic market and exports most of its products.
SKF plans to transfer the supply of products from Busan to its factories in Puebla, Mexico, Pune, India, and Shanghai, China, to localize business and support the transition to EV drivetrains.
Risk Analytics
Volkswagen has reported that an audit of its jointly owned site in Xinjiang, China, conducted by Loening Human Rights & Responsible Business GmbH, found no evidence of forced labor. The audit included inspections of employee contracts and salary payments for the 197 employees at the Urumqi plant, a joint venture with SAIC Motors.
Despite these findings, challenges in data collection within China were acknowledged. The audit comes in response to concerns raised by investors and rights groups about labor conditions in Xinjiang, a region documented for human rights abuses, including forced labor in detention camps.
The audit's outcome could impact Volkswagen's stock performance and investor relations, especially regarding environmental, social, and governance metrics. However, some skepticism remains due to the difficulties in ascertaining labor standards in the region.